Reason for occurrence

According to the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10, the human papillomavirus code is B97. 7. The code for anogenital warts of a venereal nature is A63. 0.
- Skin, mainly in the dermis;
- Mucous membrane appears on the mucosal epithelium of reproductive organs, oral cavity, etc.
Infection routes and risk factors
- "vertical" transmission. This is the name given to the spread of infectious agents from mother to child during pregnancy. It is unclear whether the infection occurred prenatally or directly during delivery, but it is not advisable to perform a caesarean section in a mother infected with papillomavirus. Cesarean section is chosen only if there is bleeding from papillomas in the birth canal.
- The path to sex.Infections can enter the body during vaginal, oral or anal sex. The pathogen is also spread through saliva during kissing. Using a condom during sex does not guarantee protection from the virus, but it does reduce the likelihood of spreading it.
- Home style.This mechanism of disease transmission is quite rare. Infection may result from contact with a patient's personal belongings. Since the virus is present in saliva and urine, it is possible to become infected by using other people's utensils, shared towels, personal hygiene items, toilet rims, or bathrooms.
According to statistics, human papillomavirus exists in the body of more than half of sexually mature people, but in most cases it does not manifest itself in any way, but exists in a carried form.
- Premature initiation of sexual activity;
- Frequently changing sexual partners;
- Be not more than 25 years old;
- Sexual contact with someone who has had human papillomavirus or other sexually transmitted diseases;
- Pregnant;
- Imbalance of vaginal flora;
- any chronic disease;
- Endometriosis;
- Treatment with cytostatic or glucocorticoid drugs;
- excess weight;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and disruption of insulin production;
- Vitamin deficiency.
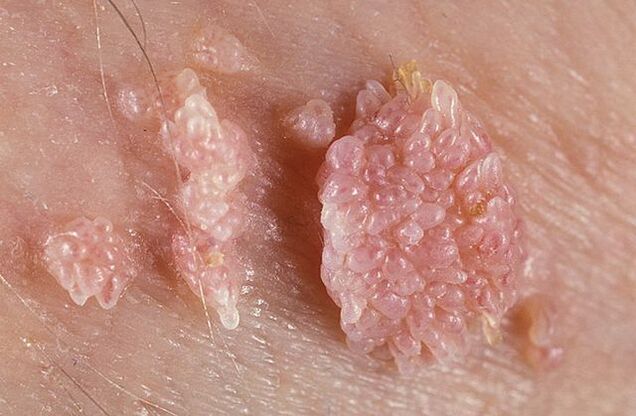
Development methods
- Hidden period. At this stage, the carrier is unaware of the presence of the infectious agent because there are no clinical manifestations. However, at this stage, a person is already contagious and can infect his or her partner through sexual contact. This incubation period can last from 2-3 months to several years.
- Illness occurs when the virus has sufficiently multiplied in the body or when the immune system's protective mechanisms decline. During this period, the first symptoms appear.
- With active development, symptoms increase.
- Self-healing, complete disappearance of papillary warts (most often observed after the end of pregnancy);
- The disease progresses slowly and lacks growth of skin hyperplasia;
- Active dynamics of papillomas, increase in shape, size, number, and merging of adjacent groups;
- Benign growth degenerates into malignant growth.
Types of genital warts
- exogenous- Protruding from the skin or mucous membrane surface, preferentially growing outward;
- endogenous- Mainly grows deep within the skin structure and is therefore barely noticeable on visual inspection;
- Buschke-Lewenstein Education- Characterized by fast growth, large size, and frequent recurrence after a course of treatment. In this form, both external growth of tissue and damage to the deep inner layers occur.
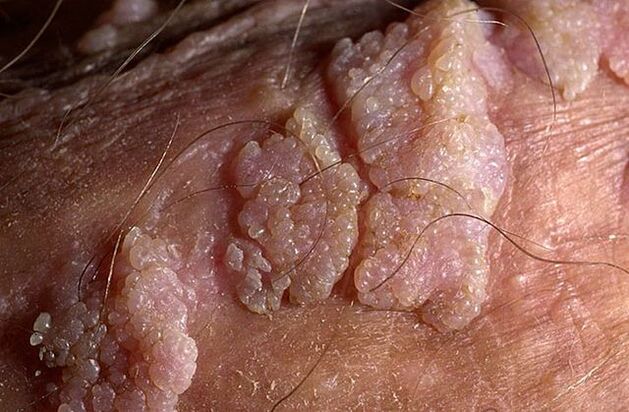
symptom
- The skin becomes slightly red and begins to itch;
- Rash in the form of blisters or small bumps on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes;
- The nodule gradually increases to 1-1. 5 cm long;
- A new rash appeared nearby, which also turned into genital wart papules.
- external genitalia;
- anal area (anogenital papilloma);
- In the urethra;
- on the cervix;
- Oral epithelium (buccal surface, tongue and inside of lips).
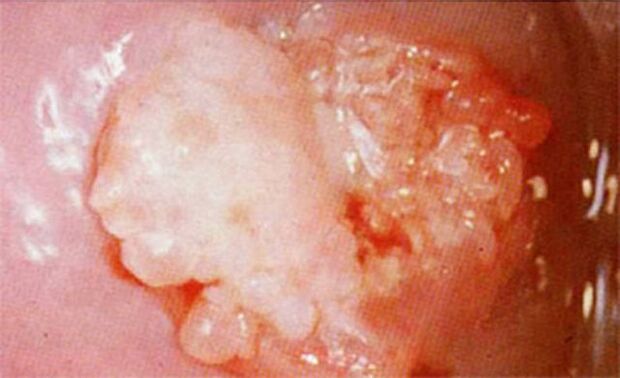
- Itching or burning sensation at the rash site;
- A foreign body sensation in the perineum;
- Humidity in the tumor area;
- The area where genital warts are located has a bad odor.
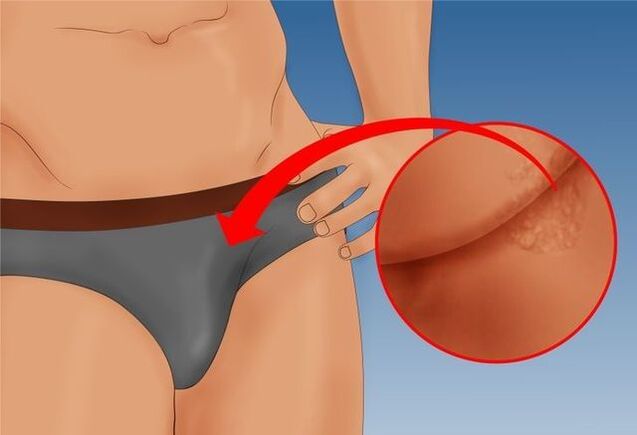
Manifestations in men
manifestations in women
50% of women who develop a white substance on their cervix during a routine colposcopy are treated with an acidic antiseptic to enhance the white color of their genital warts.
Characteristics of genital warts during pregnancy

Typically, the disease does not affect the formation of the fetus, but its effects extend to the mother's condition and the delivery process. If other infections are present, there is often a risk of premature delivery.
diagnosis
- The time when the patient first experienced symptoms;
- Possible causes of infection;
- The dynamics and progression of the disease until you see your doctor.
- PCR diagnosis, allows you to detect pathogens in epithelial scrapings of the affected area and determine their quantity (also allows you to determine the virus strain);
- Anoscopy- Visually inspect the area near the anus using a magnifying glass;
- Cytology and HistologyStructural fragments used to identify atypical cells or tissues;
- growth biopsyFrom epithelial tissue for microscopic study of tissue structure;
- Antibody titer testingFor this virus;
- smearMicroscopic tumor cytology is performed from the endocervical canal and cervix.
treat
- remove growth;
- Fight viruses;
- Enhance the patient's immunity.
radical approach
- SurgeryThe shaping is performed using a scalpel under local or general anesthesia. The incision site is sutured with surgical sutures. Although this approach is considered classic, it often results in postoperative bleeding and long hospital stays, so surgical resection has become less common recently.
- Destroyed by freezing with liquid nitrogen.This method is relatively cheap and safe, and does not require anesthesia or anesthesia. After freezing, the proteins in the formation are destroyed and the nodules dry out and fall off. After a few weeks, there will be no scarring or scarring at the treated area.
- Laser removal.Although this method is safe and efficient, it requires anesthesia and is costly, so it is only used when other methods cannot be used. When exposed to the laser beam, the structure of the growing stem is destroyed. After cauterization, genital warts lose nutrients and become necrotic within a few days, and the scabs disappear. Laser removal often leaves scars.
- Electrocoagulation.This method is affordable but very painful and requires local anesthesia. The genital growths are exposed to high temperatures, during which the papillomas are cauterized. The scab will fall off on its own after a few days, leaving a scar.
- Radiosurgery.This is currently the most technical, fast and effective method, which determines its high cost. Using high-frequency radio waves, genital warts can be painlessly removed in 15-30 minutes. It does not bleed upon removal, heals within a day, and leaves no trace on the skin afterwards.
- Chemical damage.This technique is only suitable for small formations and not suitable for multiple fusions. Special powerful substances are used that cause the death of growing cells. These products are based on high concentrations of acids or bases and can cause localized chemical burns.
medical treatement
- medical productsFor wart necrosis, suitable for home use. The product should be applied to genital warts point by point for several days. Deep chemical burns can form if the medication comes into contact with healthy tissue near the growth site, so you need to be very careful with the medication. After daily application, take a short break for a few days. If the buds do not fall off, repeat the process. Medications that cause necrosis of growths include solutions and ointments.
- Antiviral agents.They can be used locally or systemically.
- immunomodulatorImprove immunity.
Immunity to genital warts does not develop after treatment, so it is possible to be infected again by a previous sexual partner.
possible complications
- Bacterial infection attaches to damaged genital wart papilloma, causing suppuration, balanoposthitis, and ulceration in the perianal area.
- Viral bacterial urethritis occurs when the urethra grows, causing urinary problems, urinary retention, and urinary tract infections.
- Hemorrhoidal bleeding and pararectitis occur when large structures develop within the anus.
- Genital warts can affect a person's sex life, causing him to refuse sexual intercourse. All of this often leads to depression and psychological problems.
- Women may experience cervical erosion and dysplasia.
- The greatest danger is the risk of benign tumors degenerating into cancer (cancer of the glans penis or cervix).
Precaution
- Use barrier contraceptives;
- maintain an appropriate level of personal hygiene;
- regular sexual partner;
- Regular examinations by a gynecologist or andrologist;
- Prompt treatment of pelvic organ diseases;
- Quit drinking and smoking.














































































